Future Article II DOWA Recycling Complex
Various metals such as copper, gold and rare metals are used in electronic appliances that support our convenient and comfortable lives. In order to realize sustainable society through effective utilization of limited resources, it is very important to collect useful metals from used electronic appliances and reuse them in new products as resources. DOWA Metal Mine, including Kosaka Smelting and Refining, plays a role of metal resource recycling pump to collect various metals from residues from smelting and refining plants and also what is called "urban mines" of electronic substrates and mobile phones in addition to major raw materials of mineral ores, and return them back to society by utilizing technologies that they have cultivated since foundation.
h2_special02_01
People nowadays pay much attention to metals in used home electric and electronic appliances such as mobile phones and PCs called "Urban Mines". Electronic substrates used in home electric and electronic appliances contain copper, gold and rare metals. Rare metals contribute to reduced size and increase performance of high-tech products and are called vitamins for industry. Output of some of those rare metals is very limited or their prospects are restricted to certain areas. Stable supply of those metals is at risk due to expanding demand for them and resource nationalism.
Useful metals extracted from those urban mines and their recycling is expected to contribute to stable supply of rare metals.
Urban Mine Issues
Although four types of electric appliances namely television sets, washing machines, refrigerators and air conditioners are collected and recycled according to the home electric and electronic appliance recycling law, small electric and electronic appliances such as mobile phones, MD players and radio-cassette recorders are abandoned as general waste and non-combustable waste. Although there are some technological and cost-related issues to be resolved in order to be able to recycle useful metals from urban mines, it is a pressing issue to establish a social system that allows smooth and effective collection of used small home electrical and electronic appliances.
 Aimed at building a social system to allow collection of used small home electrical and electronic appliances, an experimental project started in Akita Prefecture ("Koden" Collection Project). This type of experiment has spread to cities like Kitakyushu, Tokyo, Ibaraki and Minamata and the Japanese Government has started its active involvement.
Aimed at building a social system to allow collection of used small home electrical and electronic appliances, an experimental project started in Akita Prefecture ("Koden" Collection Project). This type of experiment has spread to cities like Kitakyushu, Tokyo, Ibaraki and Minamata and the Japanese Government has started its active involvement.
The DOWA group has supported Akita's "Koden" Collection Project since its start-up and has been actively involved in building a social system to allow proper collection of used small home electrical and electronic appliances.
Japan's Best Recycling Complex
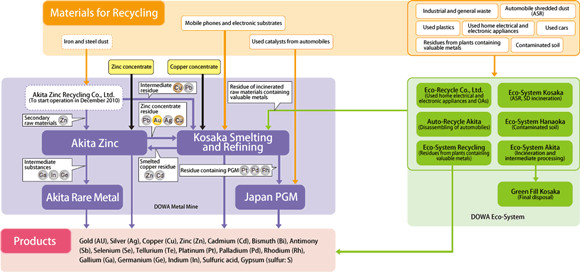
The DOWA group has established its cutting-edge technology to collect 17 different kinds of valuable metals, including not only copper and zinc but also a small amount of rare metals contained in mineral ores through its long experience in the mining and smelting business.
In the DOWA group's recycling network centering on Kosaka Smelting and Refining and Akita Zinc, 11 recycling-related companies accept and receive various types of recycled materials for extraction of valuable metals, detoxication and final disposal.
For example, Kosaka Smelting and Refining accepts mobile phones and electronic substrates as material for recycling besides mineral ores, also accepts smelting residues from Akita Zinc, incineration residues from incinerators of the DOWA group companies and low quality materials containing valuable metals to extract copper, gold or silver. Kosaka and Akita cooperate with each other in collecting valuable metals: Kosaka also supply smelting residues to Akita Zinc and Akita extracts metals such as zinc, which Kosaka cannot extract in its plants.
In this way, the DOWA recycling network forms Japan's preeminent metal recycling complex, where each plant not only collects specific metals but also accepts residues containing metals which it cannot extract as materials to be recycled for other plants to extract to enable effective collection of a great variety of metals.
Further DOWA's Initiatives
In December 2010, Akita Zinc Recycling will start operation as a zinc recycling plant. This plant will be engaged in the pre-processing of iron and steel dust from Japanese ironworks to extract zinc for reuse, and supply zinc to Akita Zinc and Kosaka Smelting and Refining as recycled material.
In this way at present the DOWA group accepts used electronic appliances and incineration residues as raw materials besides mineral ores, but we strive to develop other materials for recycling and expand the amount of materials for recycling. We also endeavor to aggressively develop technologies aimed at efficient collection and recycling of rare metals in cooperation with governmental agencies.
Kosaka Smelting and Refining - Japan's First Furnace Dedicated to Recycling
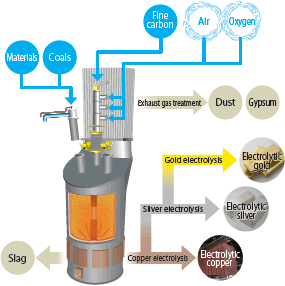
Kosaka Smelting and Refining has Japan's first furnace that can process materials for recycling containing valuable metals from electronic substrates and mobile phones (TSL Furnace) besides mineral ores.
The furnace can process zinc residues from Akita Zinc and various materials from plants of the DOWA group in addition to scraps to extract copper, gold and silver.
Kosaka is one of the major refineries of the DOWA group together with Akita Zinc and will significantly contribute to building resource recycling society in Japan.
 New refinery of Kosaka
New refinery of KosakaAkita Zinc -Zinc Refinery with the Largest Production Capacity in Japan
Akita Zinc is Japan's largest zinc refinery, producing 200,000 tons of electrolytic zinc annually. Raw materials are mineral ores from the Tizapa Mine jointly developed by the DOWA group and other parties in Mexico. Akita also accepts residues from Kosaka Smelting and Refining as materials for recycling. It will also accept materials for recycling from iron and steel dust from Akita Zinc Recycling to be operated in December 2010.
 New Sulfuric Acid Plant
New Sulfuric Acid PlantAkita Zinc produces electrolytic cadmium and sulfuric acid in addition to zinc. A new sulfuric acid plant started operation in September 2009. This plant is an eco-friendly facility that not only reduces sulfur oxides emission to the atmosphere to one fourth of the existing plant, but also significantly saves fuel (annual reduction of 1500 kiloliters fuel oil) through effective utilization of heat from sulfuric acid production.
Akita Rare Metal -Supporting Advanced Electronic Materials in Use for IT Field
Demand for rare metals such as indium and gallium is increasing as advanced materials for use in electronic. They are often contained in the intermediate substances extracted from the zinc refining process of Akita Zinc.
 Indium
IndiumAkita Rare Metal collects indium, gallium and germanium from those intermediate substances. It also extracts those metals from used ITO targets (indium and tin compound plates used for manufacturing transparent electrodes of liquid crystal panels) and recycles them, in addition to indium originated from mineral ores. It has the world's biggest share in this field.
Japan PGM -Extracting PGM from Used Car Catalyst
 Car catalyst
Car catalystPlatinum, palladium and rhodium are used as an exhaust catalyst in automobiles. Japan PGM is engaged in a business to extract these metals of the platinum group from those used as a catalyst and the intermediate substances from Kosaka Smelting and Refining, with the top share of the business both in Japan and the world.
Akita Zinc Recycling

Akita Zinc Recycling will start operation in December 2010 to process impurities other than zinc to extract zinc from iron and steel dust produced in refineries in Japan.
The solution containing zinc after being processed in Akita Zinc Recycling will be supplied to Akita Zinc as raw materials. It has a processing capacity of annual 20,000 tons (amount converted to zinc). Akita Zinc Recycling will also pre-process copper and lead that are contained in iron and steel dust and supply them to Kosaka Smelting and Refining.
In conjunction with the operation of Akita Zinc Recycling, the materials for recycling ratio of the DOWA group is expected to increase and its function as recycling complex will be enhanced.
Leader's Voice

President of DOWA Metals and Mining Co., Ltd
Nobuo Yamazaki
DOWA Metals and Mining continues to evolve as an infrastructure business company of the DOWA group.
Securing its own mines is a very important strategy for a refinery business to survive. We acquired interests in the Gibraltar Mine in addition to the Huckleberry Mine in Canada in order to secure a stable source of raw materials in 2009. As the construction work to expand the Tizapa Mine is progressing steadily, from which Akita Zinc procures raw materials, we will be able to produce 40% more at the end of 2010. In December 2010 we will start extraction of 200,000 tons of zinc per year from iron and steel dust, which will increase the amount of zinc from our own mines to 30%. Kosaka Smelting and Refining will endeavor to increase revenue and optimization by increasing the capacity of it TSL furnace and collecting nickel and tin which were not extracted before. It has the world class indium production capacity, extracting rare metals from zinc ores and ITO scrap.
DOWA Metals and Mining aims at realizing sustainable growth by extracting valuable metals from both concentrates and urban mines, while contributing to fighting against global warming and building resource recycling society.